Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
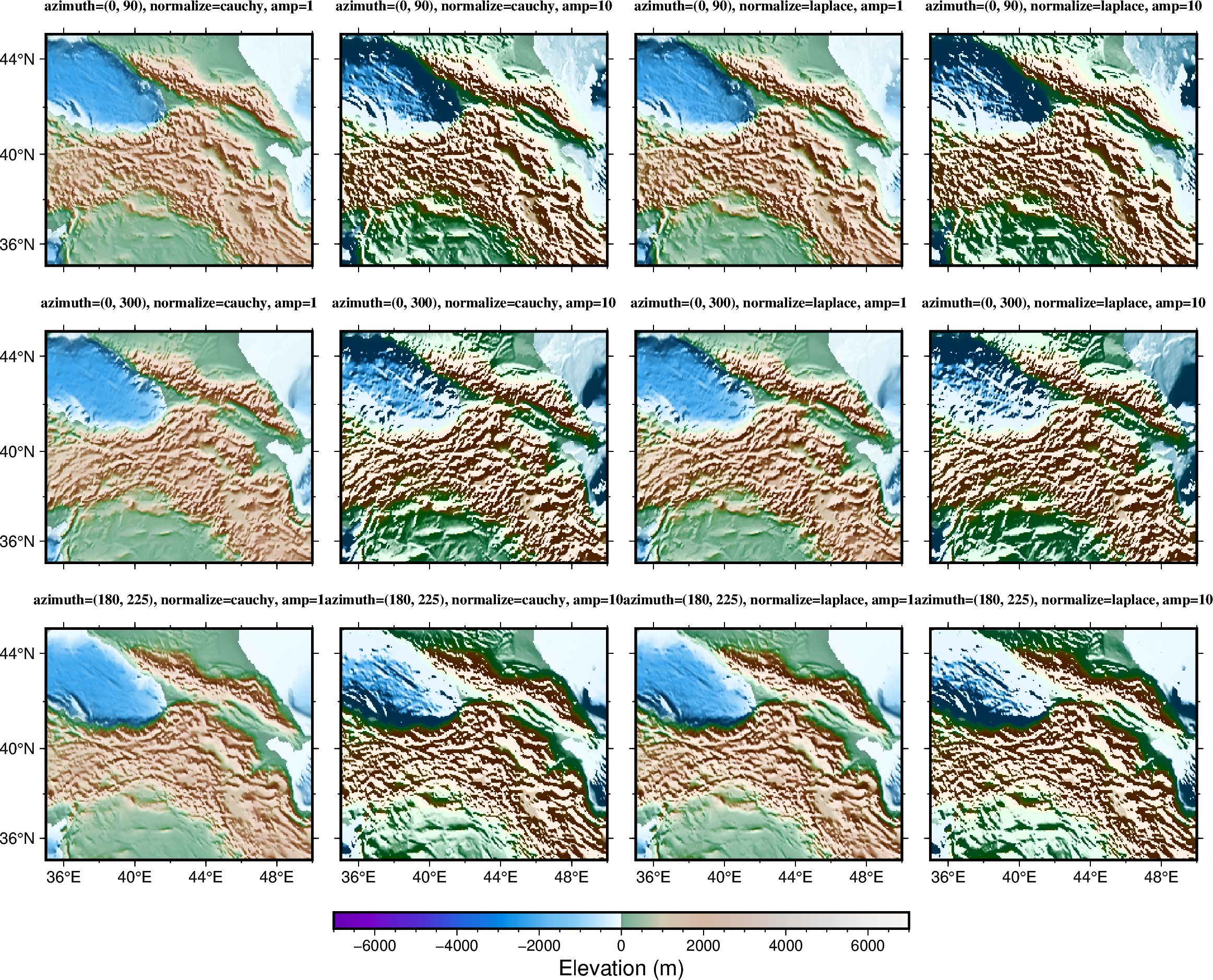
Calculating grid gradient with custom azimuth and normalization parameters
The pygmt.grdgradient function calculates the gradient of a grid file. As input,
pygmt.grdgradient gets an xarray.DataArray object or a path string to a
grid file. It then calculates the respective gradient and returns an
xarray.DataArray object. The example below shows how to customize the gradient
by setting azimuth and normalization parameters.
azimuthsets the illumination light source direction (0° is North, 90° is East, 180° is South, 270° is West).normalizeand related parameters enhances the 3-D sense of the topography.
The normalize parameter calculates the azimuthal gradient of each point along a
certain azimuth angle, then adjusts the brightness value of the color according to the
positive/negative of the azimuthal gradient and the amplitude of each point.
grdblend [NOTICE]: Remote data courtesy of GMT data server oceania [http://oceania.generic-mapping-tools.org]
grdblend [NOTICE]: SRTM15 Earth Relief v2.7 at 03x03 arc minutes reduced by Gaussian Cartesian filtering (15.7 km fullwidth) [Tozer et al., 2019].
grdblend [NOTICE]: -> Download 90x90 degree grid tile (earth_relief_03m_g): N00E000
import pygmt
from pygmt.params import Position
# Load the 3 arc-minutes global relief grid in the target area around Caucasus
grid = pygmt.datasets.load_earth_relief(resolution="03m", region=[35, 50, 35, 45])
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# Define a colormap to be used for topography
pygmt.makecpt(cmap="gmt/terra", series=(-7000, 7000))
# Define figure configuration
pygmt.config(FONT_TITLE="10p,5", MAP_TITLE_OFFSET="1p", MAP_FRAME_TYPE="plain")
# Setup subplot panels with three rows and four columns
with fig.subplot(
nrows=3,
ncols=4,
figsize=("28c", "21c"),
sharex="b",
sharey="l",
):
# Setting azimuth angles, e.g. (0, 90) illuminates light source from the North (top)
# and East (right).
for azi in [(0, 90), (0, 300), (180, 225)]:
# "cauchy"/"laplace" sets cumulative Cauchy/Laplace distribution, respectively.
for normalize in ("cauchy", "laplace"):
# amp (e.g., 1 or 10) controls the brightness value of the color.
for amp in (1, 10):
# Making an intensity DataArray using azimuth and normalize parameters
shade = pygmt.grdgradient(
grid=grid, azimuth=azi, normalize=normalize, norm_amp=amp
)
fig.grdimage(
grid=grid,
shading=shade,
projection="M?",
frame=[
"a4f2",
f"+tazimuth={azi}, normalize={normalize}, amp={amp}",
],
cmap=True,
panel=True,
)
fig.colorbar(
position=Position("BC", cstype="outside"),
length=14,
width=0.4,
orientation="horizontal",
frame="xa2000f500+lElevation (m)",
)
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.988 seconds)